Overview
Cerro Delta is a High Sulfur Au and Ag Epithermal Deposit composed of granitic to porphyry rock instructed by dacitic dome, andesitic lavas and mafic dikes. It presents zones of Advanced Argillic alterations with central zones composed of Qz-Vuggy structures with silica overlay. The surface geochemical results reached values of up to 5.75 gr/Tn.
Geophysical studies show two zones with strong to moderate IP-Resistivity that would be indicating the concentration of sulfides below the surface.
Cerro Delta is located in the Maricunga belt, considered one of the gold belts with the greatest potential worldwide. This belt has both active mines and a series of exploratory projects at different stages of development, from initial phases to feasibility. For this reason, the region is considered one of the best and richest metal belts with economic deposits in the Andes Mountains.
The Maricunga Belt
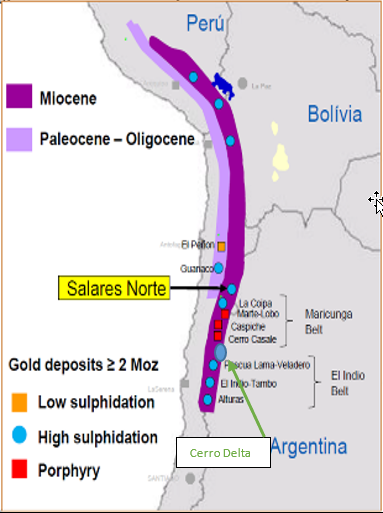
The Maricunga Belt is a linear metallogenic unit defined by at least 14 zones of gold and/or silver mineralization between latitudes 26 and 28 degrees S in the Andes Mountains of northern Chile. Total geological reserves are 420 metric tons of gold and about 14,000 metric tons of silver divided between intrusion-hosted porphyry-type deposits and high-sulfidation, acid sulfate-type, volcano-hosted epithermal deposits (Economic Geology Vol. 86, 1991, pp. 1238- 1260, Tomas Vila-Richard Sillitoe).
Vila and Sillitoe (1991) defined the region as an elongated north-south area of approximately 200 km by 50 km between 4,000 and
6,000 meters above sea level. The area contains at least six volcanic complexes aligned along the western edge of the Cordillera de Domeyko, located between Chile and Argentina.
The Maricunga belt contains a large number of porphyry-type copper and gold projects, as well as high sulphidation epithermal gold and silver projects in different stages of exploration. Some of these, near Cerro Delta, are shown in the image below.
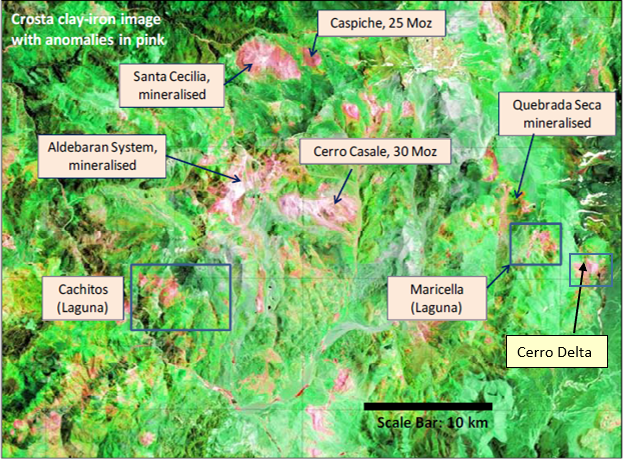
Photo Gallery
Location Map








